- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Please Choose Your Language
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-12-29 Origin: Site








How do manufacturers achieve the high level of precision needed for perfect components? The answer lies in the Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM). In this article, we’ll explore what CMMs are, the different types available, and how they function. You’ll also discover how these machines are transforming industries by enhancing both precision and efficiency in manufacturing.
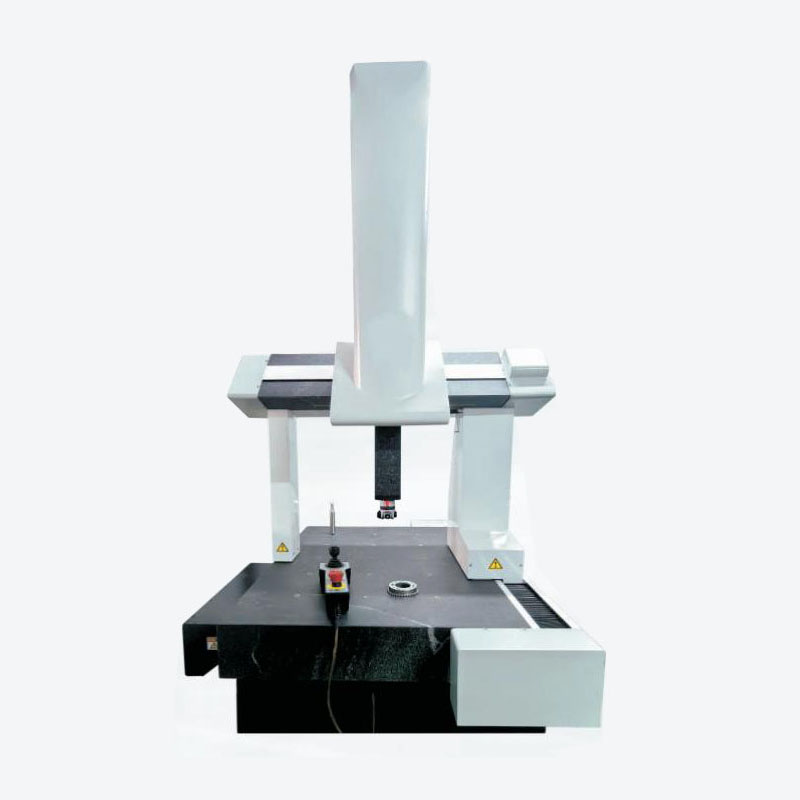
A Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) is a tool used to measure the physical geometrical characteristics of an object. The machine uses a probe, which contacts the object’s surface, to determine its location in three-dimensional space. CMMs are equipped to measure length, width, height, and other dimensions, ensuring that parts meet the required specifications.
These machines are essential for quality control, as they provide precise, repeatable measurements that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with manual measuring tools.
There are three main types of CMMs, each designed for specific environments and measurement needs:
Type of CMM | Description | Best Use Case |
Bridge CMM | Features a stationary bridge structure with moving probes along X, Y, Z axes. | Ideal for measuring parts in a controlled environment. |
Gantry CMM | A larger framework CMM, similar to the bridge type, but designed to handle larger parts. | Used for measuring large parts in industries like aerospace. |
Portable CMM | Compact and flexible machines that can be moved easily and use laser or mechanical probes. | Best for on-site measurements or when space is limited. |
A typical CMM consists of the following key components:
Component | Description |
Probe | The device that makes contact with the part’s surface to collect data. Types include mechanical, optical, and laser probes. |
Drive System | Moves the probe across the three axes (X, Y, Z), ensuring accurate positioning. |
Computer Interface | Processes the data from the probe, compares it with CAD models or predefined specifications, and provides feedback. |
CMMs work by positioning the probe over a part to collect measurement data. The probe touches specific points on the surface of the object, recording the X, Y, and Z coordinates. These coordinates are then analyzed by the CMM’s software to generate a digital map of the part. Based on this map, the machine compares the part’s measurements with the specifications to identify any discrepancies.
The accuracy of CMMs is dependent on their calibration, the type of probe used, and the environmental conditions in which they operate.
In the automotive industry, CMMs are crucial for quality control. They are used to measure the dimensions of engine parts, car bodies, and other components to ensure they meet the required tolerances. This ensures that every part fits correctly in the final assembly, reducing the risk of defects.
For example, CMMs are used to inspect parts like cylinder heads, which require high precision to perform optimally in an engine.
Automotive Parts | Measurement Focus |
Cylinder Heads | Measuring dimensions for engine fitting |
Body Panels | Ensuring correct alignment and fitment |
Chassis | Verifying the structural integrity of components |
The aerospace and defense sectors rely heavily on the precision provided by CMMs. Parts for aircraft engines, structural components, and other critical systems must be manufactured to exact specifications. CMMs help ensure that every piece meets these stringent requirements.
Given the critical nature of these applications, CMMs in aerospace and defense are often subject to high standards of accuracy, with measurement tolerances as tight as a few microns.
In the consumer electronics industry, components like circuit boards, connectors, and housings are measured with CMMs to ensure their quality. Electronics often require precise fitting of parts to avoid malfunctioning, and CMMs offer the accuracy needed for these high-precision components.
Medical devices, such as surgical instruments and implants, must meet exacting standards. CMMs are used to measure the geometry of these components to ensure they fit and function as intended. Additionally, the FDA and other regulatory bodies often require that medical devices undergo rigorous testing, making CMMs an essential part of the quality assurance process.
Medical Device Components | Measurement Focus |
Surgical Instruments | Ensuring accuracy in dimensions for safety |
Implants | Verifying shape and fit for compatibility |
CMMs offer a significant improvement over traditional measuring tools such as calipers and micrometers. These older tools rely heavily on manual operation, which can introduce human error. CMMs, on the other hand, provide automated and highly accurate measurements. They eliminate the guesswork involved in manual measurements, ensuring greater consistency and precision.
Measurement Tool | Pros | Cons |
CMM | Automated, accurate, repeatable | Expensive, requires proper calibration |
Calipers | Simple to use, inexpensive | Prone to human error, limited in precision |
Micrometers | High accuracy for small measurements | Limited measurement scope, manual operation |
One of the key advantages of CMMs is their ability to perform 3D measurements. Traditional tools can only measure along two axes, limiting their usefulness when measuring complex geometries. CMMs, however, can measure parts in three dimensions, allowing for the inspection of intricate shapes and geometries that would be difficult to assess manually.
CMMs can be integrated with Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) systems. This integration allows manufacturers to compare actual measurements with digital models in real-time, improving the efficiency and accuracy of the manufacturing process. The result is a smoother transition from design to production, with fewer errors and faster production times.
CMM Integration with CAD/CAM | Benefit |
CAD Integration | Comparing actual parts to digital models for accuracy |
CAM Integration | Streamlining production by ensuring design specifications are met |
CMMs significantly reduce the time needed for manual measurements. They can perform multiple measurements in a single automated process, improving throughput. This reduction in time leads to faster production cycles, which is especially beneficial in industries with high-volume production, like automotive or electronics manufacturing.
Benefit | Impact |
Automated Measurements | Reduces time spent on measuring components |
Increased Throughput | Faster production cycle times |
Quality control is vital in manufacturing, and CMMs enhance this process by providing consistent, repeatable, and accurate measurements. With CMMs, manufacturers can detect defects early in the production process, reducing the number of defective products that reach the final customer.
CMMs can measure a wide variety of geometries, from simple flat surfaces to complex 3D shapes. This versatility makes them ideal for industries that require the measurement of different types of parts, such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing.
Measurement Type | Application |
Flat Surfaces | Automotive parts, electronics |
3D Geometries | Aerospace components, medical devices |
While CMMs offer significant advantages, their initial cost can be high. The machines themselves are expensive, and there may also be costs associated with training operators and maintaining the machines. However, many companies find that the increased efficiency and quality control provided by CMMs justify the upfront investment.
To ensure accuracy, CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machines) require regular calibration. Calibration is crucial as it guarantees that the measurements taken by the machine are precise and reliable. Additionally, operator expertise plays a critical role in ensuring the proper use of the machine and preventing errors. Inexperienced operators or incorrect calibration can lead to significant measurement inaccuracies, affecting the overall quality and reliability of the results. Therefore, both calibration and operator training are essential for maintaining optimal performance and accuracy in CMM operations.
CMMs need a controlled environment to function optimally. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and cleanliness can affect the accuracy of measurements. Companies must provide a stable and clean environment for their CMMs to ensure the best results.
CMMs are evolving with the integration of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and automation. AI can improve the precision of CMMs by allowing them to learn from previous measurements and make adjustments in real-time. Automation will also increase the speed and efficiency of measurements, making CMMs even more valuable in high-volume manufacturing environments.
The future of CMMs also involves miniaturization and increased portability. Smaller, portable CMMs are being developed for use in a wider range of environments, including on-site measurements and smaller manufacturing setups. These machines will provide the same level of accuracy as their larger counterparts but with the added flexibility of portability.
CMMs are contributing to the rise of Industry 4.0, where connected systems communicate with each other to optimize manufacturing processes. CMMs can now integrate with smart factory systems, providing real-time feedback and allowing manufacturers to make immediate adjustments to the production process.

Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) are essential tools in modern manufacturing, offering precision, efficiency, and quality control across a wide range of industries. As manufacturing processes become increasingly complex, CMMs provide the accuracy needed to meet stringent quality standards. Forth specializes in producing high-quality CMMs that help businesses enhance their production processes, reduce defects, and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape. By understanding how CMMs work and their many applications, companies can leverage these machines to improve their efficiency and product quality.
A: A Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) is a device used to measure the physical geometrical characteristics of an object. It uses a probe to contact the object's surface and record precise measurements in three-dimensional space.
A: A CMM works by moving a probe across a part’s surface to collect data at various points. These measurements are recorded as X, Y, and Z coordinates and compared with pre-set specifications to determine if the part meets the required standards.
A: The main types of CMMs are bridge CMMs, gantry CMMs, and portable CMMs. Bridge CMMs are commonly used for small to medium-sized parts, while gantry CMMs handle larger parts. Portable CMMs are flexible and used for on-site measurements.
A: CMMs are used in manufacturing for precise measurement, quality control, and ensuring parts meet specifications. They reduce human error, improve speed, and provide consistent, repeatable measurements for better product quality.