- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Please Choose Your Language
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-05 Origin: Site








How do modern manufacturers achieve both precision and efficiency in their processes? The answer lies in the use of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines and CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines). While CNC machines automate part production, CMMs ensure those parts meet exact specifications. In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between CNC and CMM and their essential roles in modern manufacturing.

Understanding the difference between CNC and CMM is vital for optimizing production. CNC machines focus on efficiently creating precise parts, while CMMs play a crucial role in confirming that these parts adhere to required specifications. Businesses can better streamline their processes by recognizing when and how to use each technology.
Choosing between CNC and CMM depends on whether you need to manufacture or measure. CNC machines are ideal for high-speed production, while CMMs are necessary for quality control and verification, especially when complex or tight tolerances are involved.
CNC refers to the use of computers to control machine tools, automating the production process. CNC machines can perform a variety of tasks, including drilling, milling, and turning, with high accuracy and repeatability.
A CNC machine operates by following coded instructions from a computer program. The machine’s movements are directed by a series of commands that control the tool’s positioning and speed, allowing it to cut, shape, or form the material.
CNC machines come in various types based on the manufacturing process:
Type of CNC Machine | Functionality | Best Use Case |
CNC Milling | Uses rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece | Ideal for precision cutting and shaping |
CNC Turning | Rotates the workpiece while a stationary cutting tool shapes it | Best for cylindrical parts, such as shafts |
CNC Laser Cutting | Uses a laser beam to cut materials | Perfect for fine cutting of thin materials |
CNC Grinding | Abrasive grinding to achieve smooth surfaces | Used for fine finishing and polishing |
CNC machines improve manufacturing efficiency by automating tasks, reducing human error, and enhancing production speed. The precision of CNC ensures that each part is produced to exact specifications, minimizing waste.
CNC machines can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, making them versatile tools in various industries. Their ability to handle different processes like drilling, cutting, and shaping ensures they can meet a wide range of manufacturing needs.
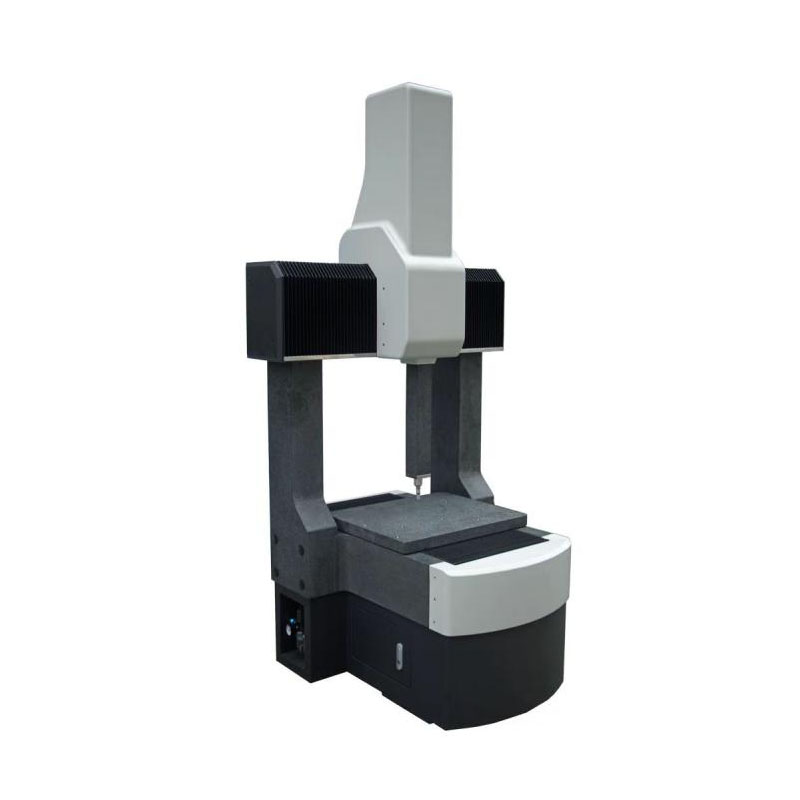
A CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) is used to measure the physical geometrical characteristics of an object. CMMs can be used to inspect and verify the accuracy of parts, ensuring they meet the exact specifications.
CMMs use a probe (mechanical, optical, or laser) to touch or scan the part's surface. It then records the 3D coordinates of each point to determine the part's size, shape, and orientation. This data is then compared against the original design specifications.
CMMs come in various configurations depending on the application:
Type of CMM | Features | Best Use Case |
Bridge CMM | Has a bridge-style structure with a probe moving across the part | Ideal for small to medium-sized parts |
Gantry CMM | Features a larger, more rigid structure for heavy-duty tasks | Suitable for large parts and components |
Portable CMM | Compact, handheld, and flexible | Best for on-site measurement and inspection |
CMMs provide extremely accurate measurements, ensuring that parts are made to exact specifications. This is especially important for industries where tight tolerances are required, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
Unlike traditional measurement tools that rely on manual inspection, CMMs automate the measurement process, reducing human error and ensuring consistency across all parts being inspected. This is critical for high-volume production environments where every part must meet exacting standards.
The core difference between CNC and CMM lies in their functionality. CNC machines are used for manufacturing parts by shaping materials, while CMMs are used for measuring and inspecting parts after they have been produced, ensuring they meet specific dimensional and geometrical requirements.
Both CNC and CMM require skilled operators. However, CNC machines generally require more frequent intervention to adjust settings for production, while CMMs primarily focus on ensuring accuracy during inspection. Both machines, though automated, depend on human expertise to achieve the best results.
CNC machines are highly effective in creating parts with precise dimensions, reducing the chances of defects during production. The accuracy of CNC machines ensures parts are fabricated to the highest standards.
Once parts are manufactured using CNC machines, CMMs play a critical role in verifying that the parts adhere to the required specifications. This ensures that parts not only fit but also function as intended.
Both CNC and CMM technologies are essential in automotive and aerospace manufacturing. CNC machines help produce high-precision components, while CMMs ensure that these parts meet stringent safety and performance standards.
CMMs are critical in the medical device industry to ensure the accuracy of parts that must meet strict regulatory standards. CNC machines are used to create these complex parts, while CMMs verify their precision and quality.
For example, CNC milling machines are used to produce engine blocks in the automotive industry. The precision of the machine ensures that all parts are manufactured to the required tolerances, ensuring optimal engine performance.
An example of CMM usage would be inspecting a turbine blade in the aerospace industry. CMMs measure the blade's complex geometries to ensure it meets the tight tolerances required for safe operation.
CNC machines are best used for producing parts efficiently, especially in high-volume environments where precision is critical. These machines are ideal for industries that need consistent, high-speed manufacturing.
CNC machines work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, making them highly versatile in various manufacturing processes.
CMMs are essential for quality control. After parts are produced, CMMs ensure that every dimension is accurate, reducing defects and ensuring product quality.
When parts involve complex geometries, CMMs are indispensable. These machines can measure intricate shapes that are difficult to inspect using traditional methods.
CNC and CMM serve different but complementary roles in manufacturing. CNC machines are used for efficient production, while CMMs ensure that each part meets high-quality standards. Together, they contribute to creating precise, reliable products. To achieve the highest level of precision and quality, industries should utilize both CNC and CMM technologies in their production workflows. Understanding when and how to use each machine is key to optimizing the manufacturing process. At Forth, we specialize in manufacturing advanced CMM solutions to help businesses achieve optimal manufacturing outcomes.
A: The primary difference is that CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are used to manufacture parts by shaping materials, while CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines) are used to measure the dimensions of parts to ensure they meet the required specifications.
A: CMMs measure the physical characteristics of parts using probes to collect data on their dimensions and compare them to design specifications, while CNC machines automate the shaping of materials into parts based on computer commands.
A: A CMM is crucial for quality control. It ensures that parts manufactured by CNC machines meet precise specifications and tolerances, verifying the accuracy and consistency of parts after production.
A: Use a CMM after part production to verify its accuracy, especially in high-precision industries. A CNC machine should be used during the manufacturing process to create the part.
A: CNC and CMM are widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and electronics, where precision and quality control are critical.